A Deep Dive into Disk Format Tool: Which is the Best Disk Formatter for Windows?
Before we get into the disk formatter or disk format tool, let’s first understand what disk formatting is.
Disk formatting is the process of configuring a storage device, such as a hard disk, solid-state drive, USB flash drive, or memory card, for effective data storage and management.
Understanding how to format a disk may be quite useful, whether you’re a tech enthusiast, an IT professional, or a casual computer user.
In this article, we will look at the technicalities of disk formatting, when users should format a disk, and provide you with step-by-step instructions to ensure a smooth disk formatting experience.
In addition, we’d like to focus on the best disk formatter to provide free yet effective disk formatting software for Windows 11/10/8/7 users to simply format a hard drive.
Why Format a Disk?
When a disk is formatted, the file system on the disk is created or recreated. This file system governs how data on a storage drive is arranged, saved, and accessed.
NTFS (New Technology File System), FAT32 (File Allocation Table 32), and exFAT (Extended File Allocation Table) are examples of standard file systems.
The storage space is split into smaller units called sectors during disk formatting, and a file allocation table or equivalent data structure is generated to keep track of the position of files and data on the disk.
This allows the operating system to read and write data to the disk, making it available for file storage and retrieval.
Formatting a disk is a necessary activity that provides several benefits, as detailed below:
a) For File System Preparation
As previously explained, disk formatting produces the file system structures required by the operating system to organize and manage files on the drive.
The storage device cannot be utilized to store data efficiently unless it is properly formatted.
When setting up a new storage device, formatting is usually the first step to getting it ready for use. This allows customers to allocate storage space before saving any data.
b) For Enhanced Performance and Efficiency
A disk gathers unimportant files, fragmented data, and errors over time, which can have a substantial influence on its performance and responsiveness.
By formatting the disk, you can solve these problems and return the drive to its original condition, resulting in quicker data access, greater system responsiveness, and smoother operations.
By carefully structuring data, disk formatting can increase storage device performance efficiency.
It enables faster read and write operations, as well as reduced file fragmentation and improved overall system responsiveness.
c) For Compatibility
Different operating systems and computer devices require different file systems to function properly.
Formatting ensures that the storage device is compatible with the specified operating system or device, allowing for data transfer and usage to be as simple as possible.
d) For Data Security and Privacy
When you format a drive, all previous data is erased, rendering it very difficult to retrieve without specialized tools.
This function is especially handy when selling or disposing of a drive since it avoids any potential data breaches or unwanted access to your important information.
Any existing data on the storage device is permanently wiped when a disk is formatted.
Since HDD formatting allows you to erase all prior data, it guarantees that unauthorized parties cannot retrieve sensitive or secret information.
e) For Resolving Disk Errors
Another situation in which formatting a disk is required is when you find persistent disk issues. These issues can present themselves in a variety of ways, including frequent crashes, file corruption, and the inability to read or write data.
Formatting the disk effectively erases any faulty sectors and file system faults, fixing these difficulties and reviving the disk’s functioning.
In certain circumstances, disk formatting might aid in the resolution of disk-related faults and problems. For example, an HDD format process can repair file system damage or faulty sectors on a drive.
When Do You Need to Format a Disk?
While disk formatting can provide considerable benefits, it is critical to understand when to format a disk. Here are a few examples of when formatting is required:
1. After installing a new storage device
When you buy a new storage device, you should format it to guarantee compatibility with your operating system and remove any previously stored data or settings that may interfere with the device’s performance.
2. Virus or malware infection
If your disk gets infected with a virus or malware, formatting it may be the most effective method of removing the unwanted program.
Because viruses may infiltrate deep into the file system, formatting the disk assures thorough elimination, leaving no trace of the infection.
3. System upgrade or reinstallation
Formatting your drive might be a wise decision during system upgrades or operating system reinstallation.
You erase any compatibility concerns or residues of the prior installation by wiping the old system files and starting again, resulting in a clean and reliable working environment.
How We Can Perform the Disk Formatting?
Now that we understand the significance of disk formatting and why it is required.
Let’s go through the step-by-step procedure for formatting a disk or drive.
It is important to remember that formatting a drive erases all existing data, so make a backup of any important information before beginning.
To quickly format the target disk, the most convenient method is to utilize a disk formatter or a disk format tool.
A disk format tool, often known as a disk formatting utility or disk formatter, is a software application or operating system function that performs disk formatting.
As previously stated, disk formatting entails building a new file system on the storage device. The basic goal of utilizing a hard disk format tool is to establish a file system on the storage device, preparing it for data read and write operations.
This procedure comprises partitioning the storage space into manageable pieces known as sectors and developing a file allocation table or a similar data structure that keeps track of the position of files and data on the disk.
It ensures data integrity by removing any existing data and preparing the storage media to accept new data in an orderly fashion.
Disk Formatting Tools
Disk format tools or Disk formatting Utilities are classified into two types: built-in operating system tools and third-party applications.
Each kind has unique features and functionalities that cater to different user demands. Let’s go through each one in more detail:
Built-in Operating System Tools:
Most contemporary operating systems include disk formatting applications that enable users to format storage devices without the use of extra software.
These built-in tools provide basic formatting capabilities and are often easy to find and use.
To format hard disks, SSDs, USB devices, and memory cards on Windows computers, utilize the Windows Disk Management program.
It lets you create, remove, and format partitions, as well as alter drive letters and file system types (for example, NTFS and FAT32).
Similarly, disk formatting utilities are incorporated into Mac OS and Linux.
In addition to this Disk Management tool, Windows has the CMD and File Explorer utilities.
However, while all three programs support NTFS and FAT32 file systems, if you want Ext, exFAT, Ext2, Ext3, or Ext4 file systems, you should use a third-party utility because integrated utilities do not.
Pros & Cons of Built-in Tools:
Pros
Cons
Third-party Disk Format Software:
Third-party disk format utilities are stand-alone programs created by third-party firms or developers.
When compared to built-in tools, these tools provide a broader range of functions and capabilities.
Among the most popular and greatest third-party disk formatters or disk format software are:
AOMEI Partition Assistant Standard: For Windows users, AOMEI Partition Assistant Standard is a free disk formatter. The use of this software is pretty straightforward. It assists you in completing the disk formatting operation in an easy and error-free manner. We have provided a step-by-step procedure for using this program as an example.
EaseUS Partition Master: This program offers full partition management, like disk cloning, and formatting options for Windows users. It supports a variety of file systems, including NTFS, FAT32, exFAT, and others.
MiniTool Partition Wizard: MiniTool Partition Wizard has capabilities comparable to EaseUS Partition Master and supports Windows and Server versions. It lets users manage partitions, convert file systems, and copy and format disks.
GParted: GParted is a free and open-source partition editor that works on Linux, Windows, and macOS. For advanced users, it has powerful partitioning and formatting options.
Pros & Cons of Third-party Software:
Pros
Cons
The choice between built-in operating system tools and third-party applications is determined by your requirements and level of knowledge.
Built-in tools are frequently adequate for basic formatting needs.
Third-party disk format software, on the other hand, may be a better alternative if you want extensive partition management, support for less popular file systems, or additional data recovery tools.
How to Use the Disk Formatter AOMEI Partition Assistant?
As previously stated, there are various third-party disk formatters on the market.
AOMEI Partition Assistant is the best disk formatted for the majority of our disk formatting tasks.
This hard disk format program is available for free download, installation, and use. By using this software, you can quickly format your hard disk.
=> After installing, open the software, Right-click a partition on the disk to be formatted, and choose the “Format Partition” option.
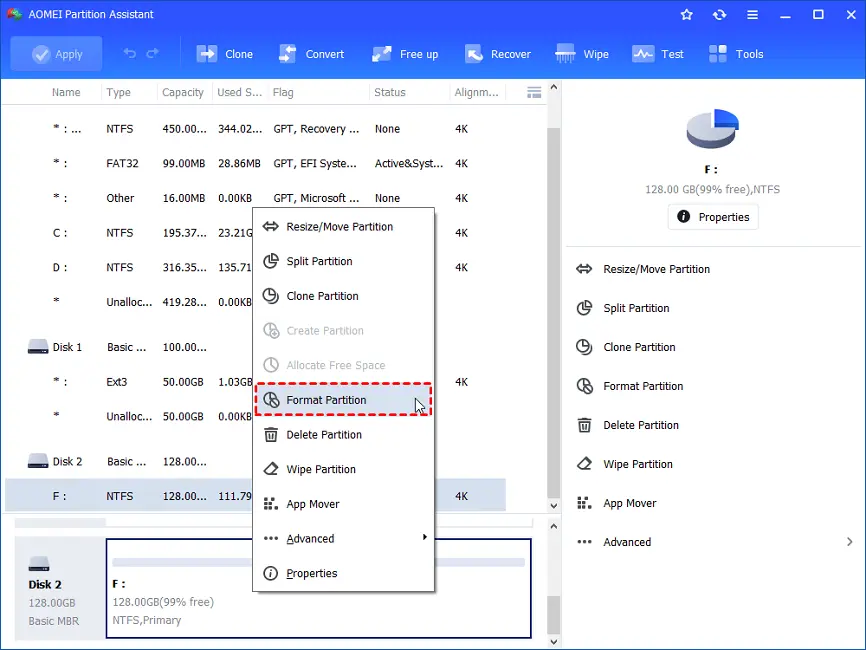
=> Set the partition label, cluster size, and file system as desired, then click “OK.”
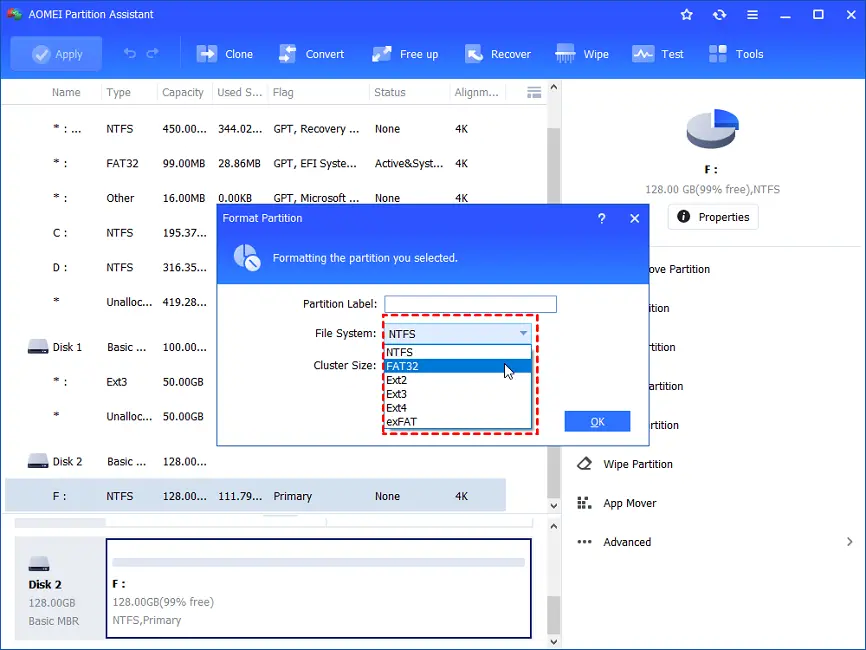
=> Begin formatting the hard disk by clicking the “Apply” button in the primary interface.
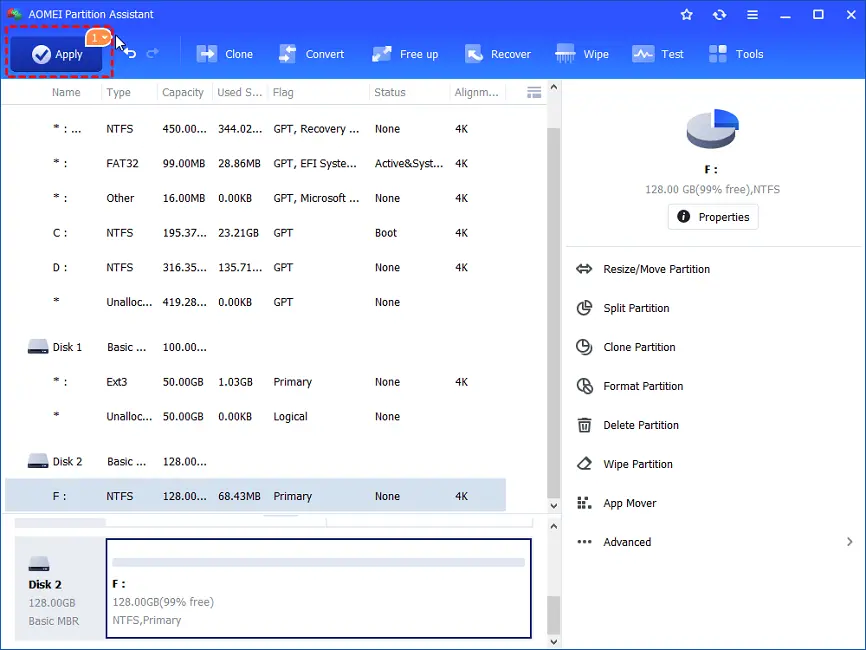
Even if the disk partition is write-protected, you can format it properly in the above three steps using this hard drive formatting program.
Important Disk Formatting Practices to Consider
It is critical to follow standard practices while formatting a drive to avoid data loss or damage.
Disk formatting, like other disk-related tasks, is potentially irreversible, and any existing data on the storage device will be permanently deleted.
So before you begin formatting, consider the following essential best practices:
- Backup Data: Always back up any vital data saved on a disk before formatting it. Make a backup of your information on an external storage device, cloud storage, or another safe location to guarantee that you can recover it if something goes wrong during the formatting process.
- Ensure Disk Health: Before formatting, make sure the disk is in good condition and working properly. Check the disk for any potential faults or errors using disk diagnostic tools. If the drive has any physical concerns, such as faulty sectors, avoid formatting until the problems are solved.
- Select the Right File System: Choose the best file system for your needs. Distinct file systems have specific features and are not compatible with all operating systems. When selecting a file system, consider aspects such as file size constraints, data security, and OS compatibility.
- Proper Disk Selection: When choosing a disk to format, exercise utmost caution. Make sure you’ve selected the proper drive, as formatting the incorrect disk might result in irreversible data loss.
- Disconnect Unnecessary Drives: Disconnect other external storage devices before formatting a specific disk to avoid accidentally formatting the wrong drive due to a misunderstanding.
- Go with Full Format: Many disk format programs include both fast and full format options. A fast format is quicker, but it does not properly check for faulty sectors, whereas a full format does. If the disk has never had any problems, a fast format may suffice. A complete format is advised for fresh disks or disks with potential difficulties.
- Use Trusted Formatting Tools: Use reputable and dependable disk format tools, whether incorporated into the operating system or third-party applications. To limit the risk of data corruption, avoid using unfamiliar or unproven tools.
- Follow the Formatting Wizard in the Tool: To avoid mistakes and ensure a successful format, if using disk formatting software with a wizard or guided procedure, carefully follow the steps offered by the program.
- Don’t Use Any Application During Formatting: Close every program, and make sure that any open files are saved and closed appropriately before formatting. It helps in the prevention of data corruption caused by unanticipated write operations during the formatting process.
- Don’t Shut Down the PC: Once the formatting procedure has begun, do not interrupt or shut down the system until it is finished. Disruptions during the formatting process might result in data loss or disk corruption.
- Cross-check the Format Completion: After formatting, verify that the operation was successful and that the disk is in the appropriate format. Check that the system successfully identifies the formatted disk.
By following these recommended practices, you may limit the chance of data loss or corruption and ensure a smooth and effective formatting procedure.
Remember that formatting should be done with caution and only when required.
Conclusion
In conclusion, we understood that disk formatting is an important operation that prepares a storage medium for efficient data storage and utilization.
It organizes the storage space, erases any existing data, and allows for maximum performance and compatibility with the operating system or device.
However, because it permanently erases data, it should be performed with caution by following the recommended practices for disk formatting mentioned in this article, and users should always back up essential files before carrying out disk formatting.
We hope you are interested in our articles and consider following our Facebook, Instagram, and Twitter pages for regular updates.
Subscribe to our free newsletter to get similar articles and regular updates directly in your Email Inbox.
Also, share this article with your friends and relatives. Bookmark this page for future reference.






