The Difference Between On-Grid and Off-Grid Solar Systems
As more people and companies look for environmentally friendly and sustainable fuel substitutes for fossil fuels, solar energy is growing in popularity.
On-grid and off-grid solar systems are the two main solar power-capturing technologies in this field of alternative energy. These systems have different benefits, uses, installation requirements, and working processes.
The choice between an off-grid and an on-grid system is important and is influenced by several variables, such as cost, location, and energy requirements.
The purpose of this page is to clarify the distinctions between these two kinds of solar systems, offering a comprehensive analysis to support readers in making sensible decisions.
Definition of On-Grid and Off-Grid Solar Systems
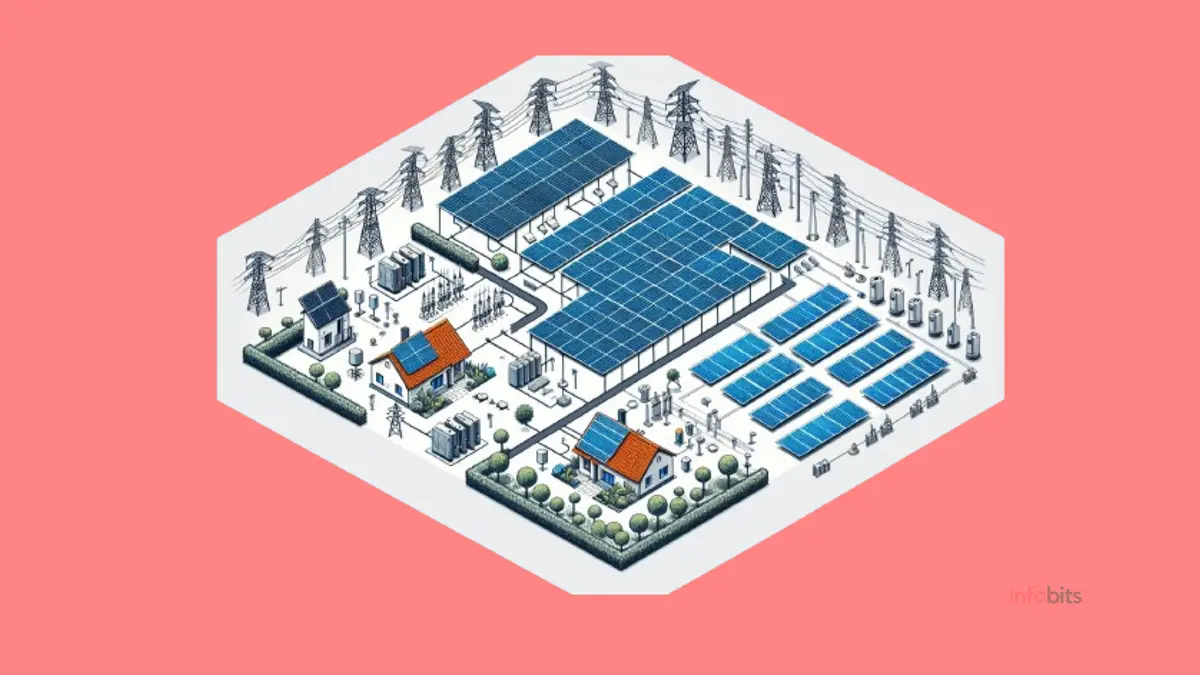
An on-grid solar system is connected to the local utility grid and is sometimes referred to as a grid-tied or grid-connected system.
With the use of techniques like net metering, this system enables homes to feed back surplus power generated into the grid and get credit.
An off-grid solar system, on the other hand, is independent of the utility grid and runs exclusively on solar panels. It also usually includes energy storage devices such as batteries.
Understanding On-Grid Solar Systems
The feature that distinguishes on-grid solar systems is their integration with the public power grid.
They are made up of solar panels, an inverter, and sometimes a power meter to monitor the amount of energy that is transferred to the grid.
On-grid systems’ main benefit is their capacity to reduce energy expenses by enabling excess energy to be sold to the utility provider.
However, because these devices must shut down for safety when the grid goes down, they are unable to supply electricity during outages.
For those who live in places with dependable utility services and rare power outages, on-grid solutions are perfect.
Many users find this method appealing because of how simple it is to connect to the grid and because of the possible financial rewards of receiving energy credits from utility providers.
Overview of Off-Grid Solar Systems
Off-grid solar systems provide total independence from the power grid. Since the grid is not a backup source, these systems need to be carefully planned to guarantee they fulfil all of a household’s or business’s energy demands.
Because they need a mechanism to store the energy for use during the hours when it is not sunny, off-grid systems are more complicated than their on-grid counterparts. Battery banks are the most popular method for achieving this storage.
Off-grid solutions work well in isolated areas when grid connectivity is either too costly or unavailable.
These systems provide you with the freedom to produce and use the power you need, and they’re a great choice for people who wish to lead more self-sufficient and sustainable lives.
However, off-grid systems are typically more expensive and difficult to maintain because of the requirement for storage and extra equipment.
Components of On-Grid and Off-Grid Solar Systems
Primary Elements of On-Grid Solar Systems
An inverter, mounting hardware, solar panels, and occasionally a monitoring device that records energy generation are the components of a standard off-grid solar installation.
An essential part is the inverter, which transforms the DC power produced by the solar panels into AC electricity suitable for feeding into the grid or use for home appliances.
An additional feature of on-grid systems might be a net meter, which records the energy transferred to and from the utility grid.
Without a battery storage system, on-grid systems are easier to build and less expensive, which makes them a better option for people who live near a reliable grid. On-grid systems usually require less maintenance because of their simplicity.
Key Features of Off-Grid Solar Systems
Off-grid solar systems need a battery bank to store power for periods when the sun doesn’t shine, in addition to solar panels and an inverter.
To prevent overcharging of the batteries, charge controllers are also crucial. Off-grid systems might use backup generators, such as diesel generators, to supply electricity when there isn’t enough sunshine for extended periods.
Off-grid systems are complicated, so sizing the battery bank correctly to satisfy energy demands during non-generating hours requires careful planning.
Because of this, compared to on-grid systems, off-grid system installation and maintenance can be more difficult and expensive.
Installation and Maintenance
Installing On-Grid Solar Systems
When installing an on-grid solar system, the solar panels are usually mounted on the ground or roof, the inverter is connected, and the system is integrated with the electrical grid.
The installation needs to be done according to local laws and standards, and it’s usually best left to qualified solar installers. An examination could be necessary before the device gets connected to the grid, according to utility firms.
On-grid installations are often simple, but to optimize the system’s performance, factors like roof angle, shading, and local weather patterns must be taken into account.
On-grid solar systems are frequently an attractive option for households due to their simplicity of installation and the possibility of government subsidies.
Maintenance Requirements for On-Grid Systems
The only maintenance needed for off-grid solar systems is the routine cleaning of the solar panels and periodic checks of the electrical connections and inverter.
When performance declines, monitoring systems can notify owners, enabling prompt repair or troubleshooting.
On-grid systems have fewer components than off-grid systems, which means there are fewer possible points of failure and maintenance issues.
Procedure for Installing Off-Grid Solar Systems
Because off-grid solar systems require extra parts like batteries and charge controllers, installing one is a more complicated procedure.
To guarantee steady power availability, off-grid systems must be properly designed depending on energy requirements and consumption patterns. For further power security, the installation can also involve setting up a backup generator.
Professional help is sometimes required for off-grid installations due to their complexity and customisation requirements. Strict adherence to local laws and regulations is essential since these systems bear full responsibility for supplying a stable power supply.
Maintenance of Off-Grid Systems
Off-grid solar systems require more frequent maintenance since they require batteries and other extra parts.
In particular, batteries need to be regularly checked, maintained, and eventually replaced. Periodic maintenance is also necessary to make sure charge controllers and inverters are operating properly.
To protect their investment, off-grid system owners should be well-versed in the operation of their equipment or rely on professional services.
For people who want to be independent of the power grid, the expense and effort are frequently justified, even if they are more demanding.
Comparison of Benefits
Advantages of On-Grid Solar Systems
The benefits of on-grid solar systems are numerous. Installing and maintaining them is affordable, and you may get credits for any extra energy you produce.
In the long run, they can result in large savings on power costs, which is beneficial financially. Furthermore, on-grid systems provide a consistent supply of energy since they are supported by the current utility infrastructure.
Those who wish to lower their power bills and carbon impact without sacrificing the dependability of conventional energy sources might use these systems.
Furthermore, the attractiveness of on-grid systems is further increased by the growing number of government subsidies for the adoption of renewable energy.
Benefits of Off-Grid Solar Systems
Off-grid solar systems are perfect for places without dependable grid connectivity because they allow you to produce and consume your electricity.
They attract people who want to live sustainably or in isolated areas since they encourage self-reliance and energy independence. An independent power system’s security is a big plus for people who have to deal with erratic grid circumstances or expensive grid connection fees.
Off-grid solutions do not require energy bills, but they come with greater initial expenses because they require batteries and other components.
Similar to on-grid systems, these technologies have the potential to have a smaller environmental effect and eventually provide financial independence from power providers.
Choice Factors and Applications
Factors to Consider When Choosing Between On-Grid and Off-Grid
The choice between on-grid and off-grid solar systems is influenced by many factors. The utility grid’s accessibility and dependability are the most important factors to take into account; if the grid is stable and usable, an on-grid system could be more feasible.
Since off-grid systems offer more energy independence and on-grid systems often have lower upfront costs, the initial investment and long-term financial goals are equally crucial.
Patterns of energy usage, the need for independence, and environmental considerations are all important factors in decision-making.
To choose the system that best suits one’s needs and objectives, it is important to evaluate all of these variables—possibly with the assistance of a solar energy specialist.
Real-World Applications of On-Grid Systems
In residential, commercial, and industrial locations where the grid is dependable and readily available, on-grid solar systems are frequently utilized.
They are ideal for factories, office buildings, and houses in towns and cities that want to lower their carbon footprints and operating expenses.
Furthermore, a lot of places include large-scale on-grid solar farms in their mix of renewable energy sources.
Real-World Applications of Off-Grid Systems
In distant residences, cottages, and communities where expanding grid infrastructure is impossible, off-grid solar systems have a role.
They are also used in movable applications, such as boats and RVs, and in disaster-prone locations to operate emergency power systems, water pumps, and distant telecommunications equipment.
On-Grid and Off-Grid Solar Systems- Comparison At a Glance
An overview of the main distinctions between off-grid and on-grid solar systems is given in this comparison chart, which covers many topics, including an overview, important components, features and advantages, installation and maintenance, cost and value, choice considerations, and applications.
| Parameter | On-Grid Solar System | Off-Grid Solar System |
| Overview | Producing power that may be consumed right away or sold back to the utility system, it is connected to it. | Works separately from the utility grid, producing energy that is then stored in batteries for consumption whenever needed. |
| Primary Elements | Solar panels, inverter, and grid connection. | Solar panels, charge controller, battery bank, and inverter. |
| Features and Benefits | Reduce dependency on grid power and may result in cheaper energy costs by producing electricity during the day. provides the opportunity to earn credits via net metering. | Provides energy security and independence by supplying electricity in isolated locations or during blackouts. makes it possible to use renewable energy sources outside the grid. |
| Installation & Maintenance | Solar panels are installed by connecting them to the grid; other than the occasional cleaning, there is often little maintenance needed. Usually, maintenance entails making sure panels are clean and inspecting connections. | Additional parts, like batteries and a charge controller, are needed for installation. Checking connections, keeping an eye on the condition of the batteries, and making sure the system is operating correctly are all part of routine maintenance. |
| Cost and Value | Because battery storage is not required, initial expenditures are reduced. may offer financial advantages by way of possible energy bill reductions and net metering. | Because battery storage is required, the initial expenses are higher. offers long-term benefits by becoming energy-independent and perhaps avoiding the costs of connecting to the grid in distant locations. |
| Choice Factors and Applications | Ideal for homes looking to save energy costs and invest in renewable energy in urban or suburban locations with dependable grid connectivity. | Ideal for anyone looking for energy independence and backup power during blackouts, as well as for isolated or rural locations without connection to the grid. |
Conclusion
In conclusion, it is critical to understand the differences between off-grid and on-grid solar systems, since each presents different benefits and difficulties.
The affordability and dependency on the grid that characterize on-grid systems make them easy to deploy and maintain.
Off-grid solutions provide energy independence and the possibility to live off the land responsibly, although they are more complicated and initially more expensive.
The decision between these systems is based on several variables, including personal ideals, financial concerns, and geography.
Our sustainable energy future will be greatly influenced by the choice between on-grid and off-grid solar, as solar technology develops and becomes more widely available.
We hope you are interested in our articles and consider following our Facebook, Instagram, and Twitter pages for regular updates.
Subscribe to our free newsletter to get similar articles and regular updates directly in your Email Inbox.
Also, share this article with your friends and relatives. Bookmark this page for future reference.
You May Be Interested to Read:
- How to Select Solar Panels for Home or Office in India?
- How To Convert A Normal Inverter To A Solar One with A Solar Conversion Kit?
- Comparing C10 vs C20 Batteries for Inverters: Which One is Good?
- Best Inverter Battery for Home Use in India: An Ultimate Guide
- Lithium Battery Advantages in Inverter and UPS Systems