BLDC Fan vs Normal Fan | Why Do We Need to Use BLDC Fans?
Bulbs and fans are at the top of the list of electrical items that last the longest in our homes or workplaces.
For many years, standard ceiling fans were equipped with the same induction motor mechanism, which consumes an average of 80-85 watts.
The ceiling fan industry is going through a similar transformation as in the case of the migration of LED bulbs from normal CFLs or incandescent bulbs.
We haven’t changed our minds about the fan, which may be the second most frequently used item in our home or office after the lamps.
A ceiling fan is used for at least 8 hours per day in a typical home or workplace. Each day, the ceiling fan consumes at least 0.64 kWh of energy and requires 80 to 85 watts of power.
Surprisingly, the power supply authority regulates the fan in certain families! This is due to, the fan, which is still running all day and night and will only sleep when the electricity goes off. Fans account for a sizable portion of a household’s energy bill.
Is there a way to resolve this? Yes, by using the BLDC fans.
A new technology known as BLDC motor has emerged in recent years to make fans use less energy while maintaining a high level of air delivery. We’re attempting to explain the emergence and necessity of BLDC fans in India here.
What Is a BLDC Fan?
BLDC Motor is an abbreviation for Brushless Direct Current Motor. In this technique, permanent magnets replace rotor windings. These motors are used in electric cars and machine drives due to their high performance and dependability.
BLDC motors or BL motors are also known as electronically commutated motors (ECM or EC motors).
For many years, BLDC technology has been on the market and is widely used in industries that require high-torque motors. So far, its application to ceiling fans has been insufficient. However, as of today, this is rapidly changing.
BLDC Fan vs Normal Fan
Now we understand the basics of BLDC fans. In this session, let us go through the comparison of BLDC fans vs normal fans.
The BLDC motor revolutionized the fan industry. And it’s only a matter of time before most induction motor fans are replaced with intelligent, super-efficient BLDC fans.
As previously stated, ordinary induction motors are used in standard ceiling fans, whereas BLDC motors replace induction motors in BLDC fans. In terms of energy efficiency, BLDC ceiling fans have recently surpassed LED lights, putting them at the forefront of the market.
Related: Best Ceiling Fans Under 1500 In India
The brushless DC fan employs brushless DC motors (BLDC motors) with a cross pattern of four permanent magnets installed on the sides of the rotor. BLDC motors, unlike brushed DC motors, do not require a commutator or a brush to function.
To allow for rotational motion in a brushed motor, a commutator changes the direction of current in a motor winding. Because brushless DC motors do not require brushes or commutators, there is no arcing or brush/commutator wear and tear.
The coils aren’t even attached to the rotor. The rotor is instead a permanent magnet, and the coils are fixed to the stator. Brushes and a commutator are not required because the coils are stationary. This is an important difference between BLDC fans and normal fans.
The brushless DC fan consists of a powerful BLDC motor, a shaft, and a fan blade. These fans are powerful, efficient, and cost-effective. As previously stated, they do not generate in-circuit sparks and operate quietly.
Due to the high initial torque generated by DC motors, the brushless DC fan quickly reaches its full capacity. The only way to control their speed is to change the voltage input.
Brushless motors have a higher power-to-weight ratio, higher RPM, and electronic control, and require less maintenance than brushed motors. Brushless motors are used in a variety of applications, including computer peripherals, portable power tools, and vehicles ranging from model planes to automobiles.
BLDC motors have enabled direct-drive systems to replace rubber belts and gearboxes in the latest washing machines.
The following section will look at the constructional differences between a BLDC fan and a normal fan, as well as how they work.
What Is the Operation of a Normal Fan?
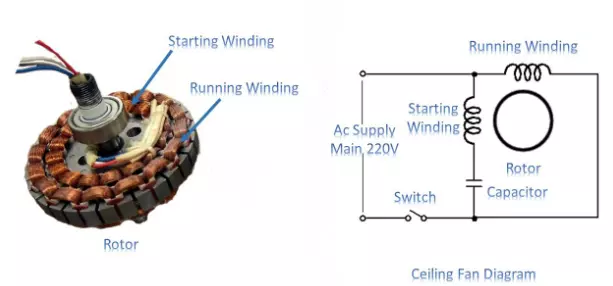
As we discussed earlier a standard induction motor is being used in a normal fan. An induction fan is made up of two key components that drive the fan’s rotational motion:
- Stator
- Rotor
Induction motor fans have coils/windings on the stator and the rotor. Electric flux is produced when current flows through the stator winding. This current flows through the coil according to the stator arrangement.
All of this is accomplished sequentially by generating a magnetic field to generate a rotational moment. Because of current induction through the rotor coils, the motor spins.
A regulator controls the speed of an induction fan, which is available in two varieties:
Resistance-based: The resistance of the regulator is varied in this method to change the voltage applied to the fan. These regulators are inefficient because they dissipate a large amount of energy as heat as an outcome of resistance, resulting in power losses.
Voltage-based: A modern regulator is essentially an on/off switch that constantly chops the voltage to adjust the fan speed. If you want to use a regulator for a standard fan, always go with these modes, which are widely available on Amazon.
How Does the BLDC Fan Function?
A BLDC fan receives an AC voltage and internally converts this to direct current (DC) using an SMPS. The mode of commutation is the primary difference between BLDC and conventional DC fans.
Commutation is the process of correcting the current direction in a motor to produce rotational motion. Because a BLDC motor has no brushes, the electronics driving algorithm allows for commutation.
The main advantage is that brushed motor commutators wear and tear over time due to mechanical contact; this is not the case in a BLDC motor, making the motor more stable for long-term use.
In other words, BLDC technology achieves its efficiency and output by combining permanent magnets and electronic circuitry.
A BLDC fan is made up of three major parts:
- Stator ( Permanant Magnets)
- Rotor (Windings)
- Electronics circuitry
A driving algorithm in the electronics circuitry drives the BLDC motor. A BLDC motor’s magnet location is sensed by an electronics circuit that uses either a Hall effect sensor or back EMF.
Because Hall effect sensors have known drawbacks, modern BLDC motor fans use the Back EMF method for switching over the period.
To explain how the BLDC fan works in simpler terms, consider the following video of a donkey with a carrot tied to his head:
Consider the Stator to be a carrot and the donkey to be a magnet. The polarity of the stator will continue to shift as a result of the magnets’ attraction, producing a rotational moment, just as the donkey in the video tries hard to reach the carrot.
Modern motors induce the other two phases to generate repulsion to increase the torque of the motor. The permanent magnets in the rotor of a BLDC fan are responsible for reducing energy consumption by weight relative to the windings in the stator.
Another advantage of using an electronic circuit in a BLDC fan is that you can incorporate several additional features to improve functionality, such as sleep mode and timer mode, both of which are compatible with home automation systems.
Many BLDC ceiling fans, unlike conventional regulators, are controlled by a remote, lowering the cost of purchasing a separate regulator. A BLDC fan can save up to ₹ 1000-1500 per year in energy costs when compared to a standard induction fan.
Furthermore, because the motor is not heated, the life of a BLDC fan is expected to be significantly longer than that of conventional fans.
While standard ceiling fans use 80-85 watts of electricity, BLDC fans produce the same amount of airflow while using half the energy.
BLDC fan power consumption is 25 to 35 watts on average. Let’s take a look at the advantages and disadvantages of being a BLDC fan.
Advantages of a BLDC Fan
- The power consumption is half that of conventional fans.
- All of the leading BLDC fans on the market today can be controlled and turned on and off using a remote.
- Relatively quiet operation.
- When the speed of a normal fan is controlled by an electronic regulator, the power consumption does not decrease proportionally. This means that if the regulator is cut in half from its maximum speed, the power consumption of normal fans is not cut in half, but is slightly slower. On the other hand, the power consumption of BLDC fan regulators decreases proportionally to the lower speed.
- It, like LED bulbs, can operate at 100 to 250 volts. The speed of a normal fan decreases significantly as the voltage drops.
- Because the power consumption of the BLDC fan is deficient when using an inverter power system, the battery backup doubles as compared to a normal fan. In general, BLDC fans will be an asset because the fan’s smooth operation is primarily aimed at inverter customers. The energy required for a standard fan can be used to power two BLDC fans without increasing the inverter’s or battery’s capacity.
Disadvantages of a BLDC Fan
- A BLDC fan is at least twice as expensive as a standard ceiling fan. BLDC fans can be purchased from a variety of companies for Rs 2500 and up.
- LED bulbs are typically damaged as a result of electronic drive circuits being ignited by lightning. Similarly, because the heart of BLDC fans is also an electronic circuit, it is impossible to predict how lightning-resistant they will be.
One thing is certain: the cost of a BLDC fan will be repaid in two to three years. In any case, at least a three-year warranty will be an added benefit.
Related: Does the BLDC Fan Have Lightning Protection, and If Not, How to Protect It?
Energy Consumption and Money Savings by BLDC Fans
A typical induction-based fan consumes approximately 80 watts, whereas a BLDC fan consumption is nearly 30 watts.
A fan, unlike a lamp, is an appliance that runs the majority of the time when the temperature is high and there is no regular inflow of cold air.
We can calculate the energy cost by assuming they run for at least 8 hours every day for 365 days. Assume that the average price per unit of energy for residential customers in India is around ₹ 7.
The cost per unit varies greatly depending on the state, power distribution company, tariff slab, and whether the unit is used for commercial or residential purposes. For our calculations, we should assume prices of around ₹7 per unit.
Assume a normal fan operates for 8 hours per day, 365 days per year. Consider its power to be 80W and its energy cost to be ₹7/kWh.
Then the total unit of energy = 0.08 x 8 x 365 = 233.6 Units
Annual Energy cost for a normal fan = 7 x 233.6 = ₹ 1635.2
But if we use a BLDC fan having a power rating of 30W,
Then the total unit of energy = 0.03 x 8 x 365 =87.6
Annual Energy cost for a BLDC fan = 7 x 87.6 = ₹ 613.2
Savings in Annual energy cost = ₹ 1022
By only using it for 8 hours per day, we saved ₹1022 over a year. But all we know is that we typically use ceiling fans for more than eight hours per day.
On average, using BLDC fans, you can save around 2000 rupees per year. When purchasing a BLDC fan, the price difference is typically around 1500 rupees, i.e. BLDC fans begin at around 3,000 rupees, whereas standard fans are priced at around 1,500 rupees.
In other words, if you run your fans for more than 15 hours per day and the cost of power per unit is greater than ₹7, you can expect to recoup your investment in a BLDC fan in less than two years.
Furthermore, the majority of BLDC fan manufacturers offer a 3-year warranty. That is the energy-saving capability provided by BLDC fans.
So, why do you waste electrical energy and money using normal fans?
Related: Best BLDC Fans in India | How to Select a Good BLDC Fan?
Some of India’s leading brands include Luminous, Havells, Super Fan, Atomberg, Crompton, and Orient. The main competitors in terms of features are Super Fan and Atomberg Fan.
Although there is no significant difference in power consumption, they differ in terms of features and warranty period.
The remote control on the Atomberg fan has more features than the Superfans. The Superfan has a simple remote with only five-speed control buttons, whereas the Atomberg fan has a timer. This means that the timer can be used to control the length of time the fan runs.
The Superfan is more appealing than the Atomberg BLDC fan is looking. Super Fan’s speciality is the availability of leaves in a variety of colours. When it comes to energy efficiency, the Atomberg fan is one step ahead.
Atomberg fans have a three-year warranty, while Super Fan and Crompton have a five-year warranty. In any case, before making a purchase, inquire about after-sales service in your area.
Energy Efficiency of BLDC Fans
An electrical equipment’s energy efficiency is defined as the ratio of output energy to input electrical energy. It is the capability of air delivery in the case of an electrical ceiling fan.
Efficiency will also be improved if internal operational losses are reduced. In the case of BLDC fans, they can deliver more air while using less energy and incurring very little operational loss.
A BLDC fan’s high efficiency means that it provides the same or more benefits while using less energy than traditional ceiling fans with single-phase induction electric motors.
Because aluminium is less expensive than copper, most popular fan manufacturers use aluminium windings instead of copper in their fans. Aluminium, on the other hand, is less energy efficient.
The Bureau of Energy Efficiency (BEE ) is the government agency in charge of promoting, developing, and monitoring various energy-efficiency projects. BEE launched the Super-Efficient Equipment Program (SEEP) in February 2012.
The Super Energy Efficiency Program (SEEP) is a program designed to accelerate market transformation for superefficient appliances by providing financial incentives in new directions at critical points of intervention. The ceiling fan has been chosen as the first item to be installed as part of this initiative.
SEEP for ceiling fans aims to surpass an efficiency level approximately 50% higher than the market average by providing fan manufacturers with a time-limited incentive to develop super-efficient (SE) fans and offer them at a lower price.
Numerous entrepreneurs have proposed the concept of BLDC fans,’ which are more energy-efficient, since the program’s inception.
Following the introduction of the BEE’s SEEP, manufacturers were required to increase copper content and improve blade designs to improve energy efficiency.
Most BLDC ceiling fans are 5-star certified and use 25-40 watts of energy, which is 40-70 per cent less power than standard fans.
Difference Between BLDC Fan and Normal Fan-At a Glance
| Parameters | BLDC Fan | Normal Fan |
|---|---|---|
| Motor Used | Brushless motor | Induction motor |
| Functioning | Uses Direct Current (DC) | Uses Alternating Current (AC) |
| Power Consumption | Around 25-30 W | Utilise up to 80 W |
| Speed Regulation | Through remote controller | Using regulator |
| BEE 5-star certified | Comparatively less | No BEE certification |
| Speed (in RPM) | 330-400 | 300-380 |
| Noise during operation | Noise increases with ageing | Noise increases with aging |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance | Comparatively high maintenance |
| Price | High initial cost | Comparatively lesser price |
| Failure chances | More susceptible to lightning | Less susceptible to lightning |
Future of BLDC Fans India
When people are aware of the benefits of a product, there is a high demand for it. When there is a high demand for a product, it is manufactured in large quantities.
When a product is mass-produced, the cost of any new technology falls. When more people start purchasing BLDC fans, the technology and price will also fall to a level that the average person can enjoy.
LED bulbs were extremely expensive between the years 2000 and 2010. We had to pay around 300-350 rupees for 7-9 W LED bulbs at the time. Many people were enticed to use LED bulbs after learning about their benefits and participating in government-sponsored promotions.
In the case of BLDC fans, similar or even greater adoption is taking place. People’s interest in BLDC fans is increasing at a linear rate. Some are attempting to comprehend its benefits, while others have already purchased at least one sample BLDC fan to evaluate it.
The high price constraint is the main reason why people avoid purchasing a BLDC fan. Despite being twice as expensive, they pay for themselves much faster than many other energy-saving solutions.
The extra Rs 1500 spent on a fan in a city like Bangalore or Mumbai is repaid within a year. In most other cities, it takes only two years, depending on our usage and energy costs.
As previously stated, the initial cost of BLDC fans is currently higher, but when we consider the rising cost of power, choosing a super-efficient 5-star rated BLDC fan makes a lot of sense.
With the BEE tightening the requirements for achieving a 5-star energy certification, the newest certified models are exceptionally energy-efficient, requiring only 25-35 watts of power.
So, if there are high-quality BLDC fans with good customer support, we hope that within 5 years, the majority of our conventional fans will be replaced by BLDC fans.
Frequently Asked Questions
Yes. BLDC fans are far superior to standard fans. Normal fans require more electricity than BLDC fans since they employ AC motors.
A BLDC ceiling fan costs at least twice as much as a normal ceiling fan. Because BLDC fans have an electronic circuit at their heart, it is hard to anticipate how lightning-resistant they will be.
BLDC fans can rotate in the reverse direction. A ceiling fan pulls down cold air in the forward direction, which is beneficial in the summer.
In the opposite direction, a ceiling fan pushes hot air down, which is useful in the winter. The majority of branded BLDC ceiling fans have a reverse feature.
Yes, the BLDC fan is quieter than a normal induction fan.
However, if the BLDC fan is broken or damaged during transportation or installation, it may make noise. Also, after a few months of use, the BLDC fan may make noises due to internal elements such as the magnet’s moves.
However, if you purchase a high-quality BLDC fan, you may never hear any noises and it will run silently.
Both BLDC and standard fans have roughly the same capacity in terms of air delivery. However, a BLDC fan will provide faster speed while requiring less power.
BLDC fans produce the same amount of airflow while using less energy. They can save up to 65 per cent more energy than standard induction motor-based fans because they remove losses caused by the mechanical friction of the brushes.
Because they lack brushes, BLDC fans are more efficient than standard fans, reducing friction and increasing fan lifespan. They are also silent and generate less heat than standard fans. BLDC fans, on the other hand, are often more costly than conventional fans.
We hope you find this information useful, and please share it with your friends and relatives.
Subscribe to our free newsletter so that you will get similar articles and regular updates directly in your Email.
Also, consider following our Facebook and Twitter pages for regular updates.
Disclosure: If you follow our links to a retailer’s website and make a purchase, we will get an affiliate commission on some, but not all, of the products or services we mention. This will not affect your pricing.








Yes we are using 3 nos bldc fan for last 3 years, saves lot of electricity bills. Thank you.