Is It Really Worth Buying a Three-Phase Inverter?
A constant power source is required for operating industrial loads such as office equipment, powering petrol stations, banks, and small to big companies, or running heavy appliances such as air conditioners, freezers, and cold storage.
Until recently, generators were the primary source of power backup for high-load applications. This is no longer the case; with advancements in inverter technology, inverters now outperform generators.
Some of us are still considering whether or not to replace our original generator system with a three-phase inverter.
An inverter is a type of power electronic equipment that converts energy from one form to another, such as direct current to alternating current, at the correct frequency and voltage.
Related: What is an inverter and how does it work?
This may be classified depending on the point of supply as well as the power circuit’s associated architecture.
As a result, they are divided into two categories: voltage source inverter and CSI (current source inverter).
In the VSI-type inverter, a lower impedance DC voltage source is employed at the inverter’s input terminals. A high-impedance DC supply is employed in the CSI-style inverter.
This article’s goal is to describe a three-phase inverter, including its circuit, function, and applications.
What Exactly Is a Three-Phase Inverter?
A system that converts direct current (DC) to alternating current (AC) is known as an inverter (AC).
Different types of inverters have also been discussed. A three-phase inverter is used to convert direct current electricity to three-phase alternating current power.
This kind is commonly used in high-voltage direct current (HVDC) transmission and variable-frequency driving applications.
Power may be distributed over a network using three separate currents that are out of phase with each other (three phases) in a three-phase inverter, whereas power can only be conveyed through a single phase in a single-phase inverter.
Assume your home has a three-phase electrical load system and a single-phase inverter. The inverter will be connected to only one phase in this situation.
The remaining two phases cannot be served by the single-phase inverter. A three-phase inverter system is required here.
Working Principle of a Three-Phase Inverter
A three-phase inverter is made up of three single-phase inverter switches, each of which may be linked to a load terminal.
The three switches can be synchronized to the basic control scheme, resulting in a six-step line-to-line output waveform with a single switch operating every 60 degrees of the basic output waveform.
The two halves of the square wave, positive and negative, each have a zero voltage point. Because these waveforms are exposed to PWM techniques based on the carrier, the waveform’s fundamental shape may be exploited to cancel the third harmonic and its multiples.
A basic three-phase inverter circuit schematic is illustrated below.
This type of inverter’s major duty is to convert direct current (DC) input to three-phase alternating current (AC).
A simple three-phase inverter is composed of three single-phase inverter switches, each of which can be connected to one of three load terminals.
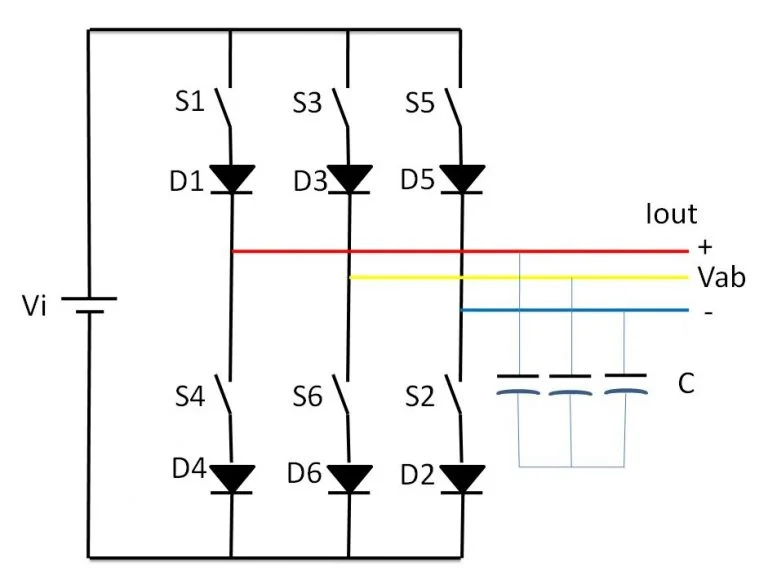
To create a three-phase AC supply, the three arms of this inverter are typically delayed by 120 degrees.
Switches on the inverter operate at every 60-degree angle, and switching occurs one by one at S1, S2, S3, S4, S5, and S6 regularly. In a nutshell, this is a three-phase inverter setup.
Applications for Three-Phase Inverters
The following are some of the uses for a three-phase inverter.
- Variable frequency drives employ these inverters (VFDs).
- This three-phase inverter technology is used in high-power applications such as HVDC power transmission.
- A three-phase square wave inverter is utilized in a UPS circuit and a low-cost solid-state frequency charger circuit.
Here the third application is employed in industrial three-phase inverters.
Related: How to Select the Right Inverter and Battery for Home in India?
Single-Phase vs 3-Phase Solar Inverter
A single-phase solar inverter has a single live wire (one phase) that connects to your household appliances. A three-phase solar inverter connects to your load via three live wires.
A three-phase solar inverter distributes electricity evenly across three wires, reducing the voltage drop problem associated with a single-phase power supply.
It should be noted that a 3-phase solar inverter will likely cost more than a single-phase inverter.
A single-phase inverter usually has a capacity of less than 5 kW. However, if you have a power demand greater than 5kW and have 3-phase wiring in your home, a 3-phase solar inverter is the best option. If your power supply is single-phase, all you need is a single-phase inverter.
Advantages of a Three-Phase Inverter Over a Generator
Modern generating inverters, as compared to generators, provide continuous power and have relatively low operating costs.
Furthermore, diesel generators must operate at full capacity, which results in significant fuel expenditures, whereas inverters operate at a reduced load.
Running generators at half load diminishes their efficiency, resulting in higher fuel consumption and shorter generator life.
Inverters, on the other hand, function consistently across all load levels and, in particular, provide improved backup time at partial loads.
Diesel generators are also notorious for emitting hazardous smoke, which contributes to increased levels of air pollution.
The Environment Pollution Control Authority of India issued an order in 2017 prohibiting the use of diesel generators in Delhi, except in the National Capital Area, when the national capital’s ambient air quality fell below dangerous levels.
The prohibition was enforced by the Supreme Court.
Inverters, on the other hand, are more ecologically friendly since they emit no hazardous smoke while powering heavy-duty applications. Another reason to prefer inverters over diesel generators!
The most extensive three-phase inverter range is provided by major inverter makers, with load handling capacities ranging from 5KVA to 100KVA, to offer power backup to multistory houses, commercial businesses, and industrial facilities with larger power requirements.
High-quality three-phase inverters have been picked by offices, showrooms, shopping malls, hospitals, elevators, hotels, schools, labs, petrol stations, banks, telecommunications poles, ATMs, and BPOs.
Frequently Asked Questions
Yes. Three-phase inverters are more complex and costly than single-phase inverters, but they produce more power, have higher efficiency, and are more stable.
Comparing a 3-phase vs single-phase inverter, three-phase power inverters are more efficient and stable.
We hope you find this information useful, and please share it with your friends and relatives.
Subscribe to our free newsletter so that you will get similar articles and regular updates directly in your Email.
Also, consider following our Facebook and Twitter pages for regular updates.